Book Appoinment
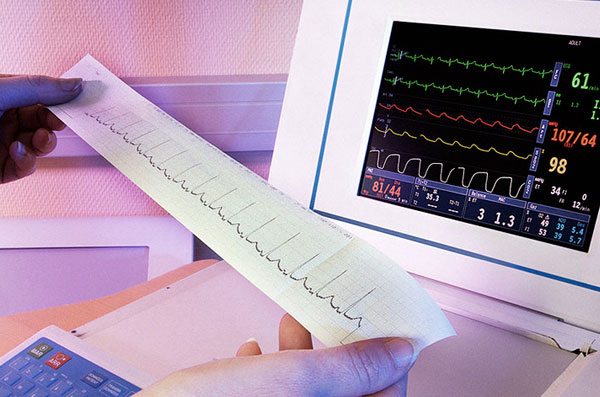
An electrocardiogram (ECG) is a diagnostic tool used to measure the electrical activity of the heart. It records the electrical signals that travel through the heart, allowing doctors to detect abnormal rhythms and heart conditions.
An ECG can be used to detect a variety of heart conditions, including arrhythmia, heart attack, cardiomyopathy, and other heart defects. It’s a simple, non-invasive test that can be performed in a doctor’s office or hospital, or at home with a portable ECG machine.
How It's Works
When an ECG is performed, small electrodes are placed on the patient’s body. These electrodes pick up the electrical activity of the heart, which is then converted into a graph called an electrocardiogram. The graph will show a doctor the electrical activity of the heart, including its rate and rhythm.
An abnormal ECG may indicate a problem with the heart’s electrical system, such as an arrhythmia or a heart attack. It can also be used to monitor the effects of certain medications or to diagnose certain types of heart disease.
